Small Molecule Reprogramming Drugs
Our patented platform technology and related IP portfolio, collectively re-create the cellular microenvironment niche in-vitro (for research) and in-vivo (for therapy). We use small molecule drugs to target this druggable entity, modulating extrinsic and intrinsic factors that influence signal transduction pathways of stem cells and somatic cells, partially reprograming their fate in the body. Using this approach, we are developing efficacious small molecule regenerative cures to a number of diseases and Aging.
CellCure is the exclusive assignee of the US Patents US9045737 (2009), US9725700 (2015), US9988607 (2017), US10584316 (2020) collectively covering Method of Use for screening, identification and Composition of Matter of pharmaceutical cocktails that partially or completely reprogram human cells, tissues, and organs. We pioneered reprogramming of human cells with small molecule cocktails and without the use of any genetic factors in 2007. We refer to the cells generated by this methodology (in-vitro or in-vivo) as Chemically induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (CiPSC®© TM, covered by the above mentioned patents). For in-vitro assays such as disease modeling and human organoid phenotypic drug screening, complete reprogramming is achieved. For rejuvenation in-vivo, partial reprogramming is enabled using specific cocktails of pharmaceuticals that reverse biological aging without the need for any gene therapy.
Unbiased Phenotypic Chemogenic Screen of drug/ compound libraries (FDA approved drugs, natural products, AI designed novel structures)
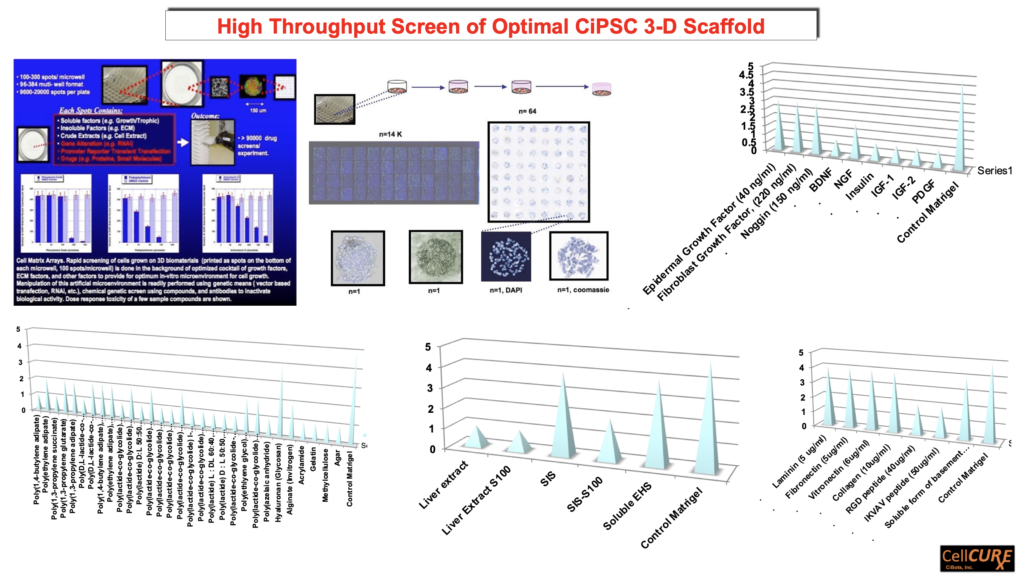
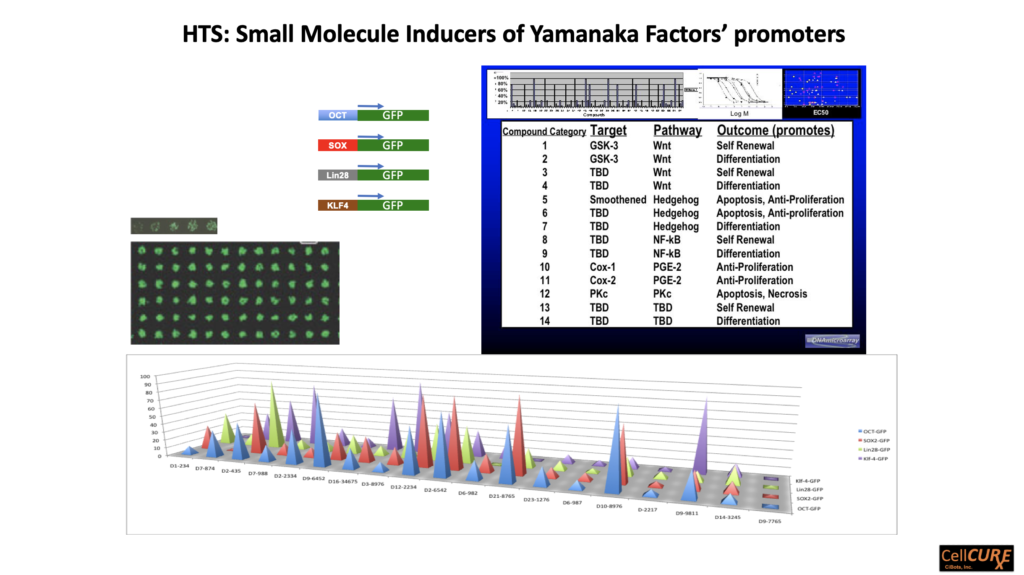
Secondary Screen in-situ of Small Molecule "Partial" or "Complete" CiPSC Reprogramming Cocktails
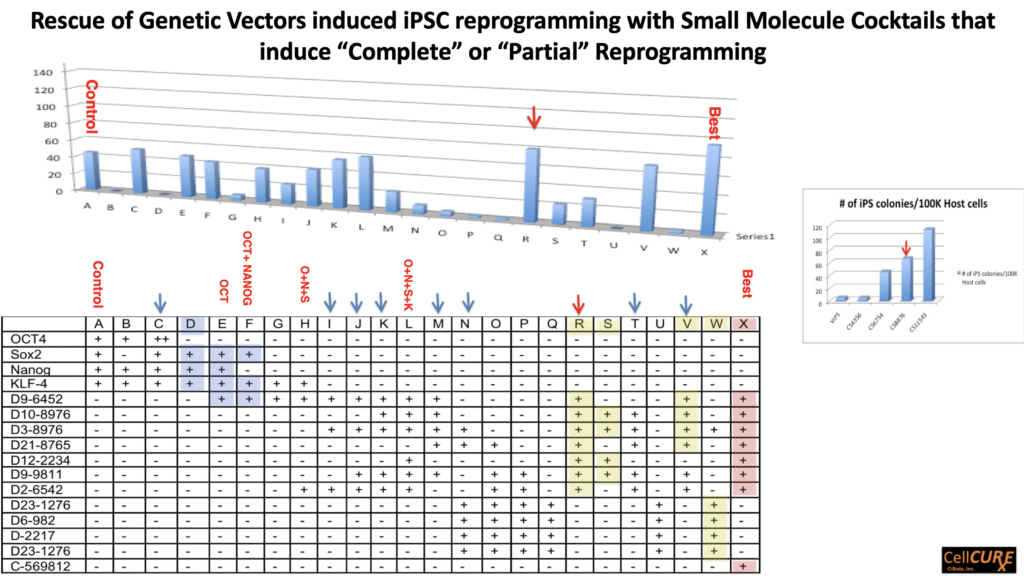
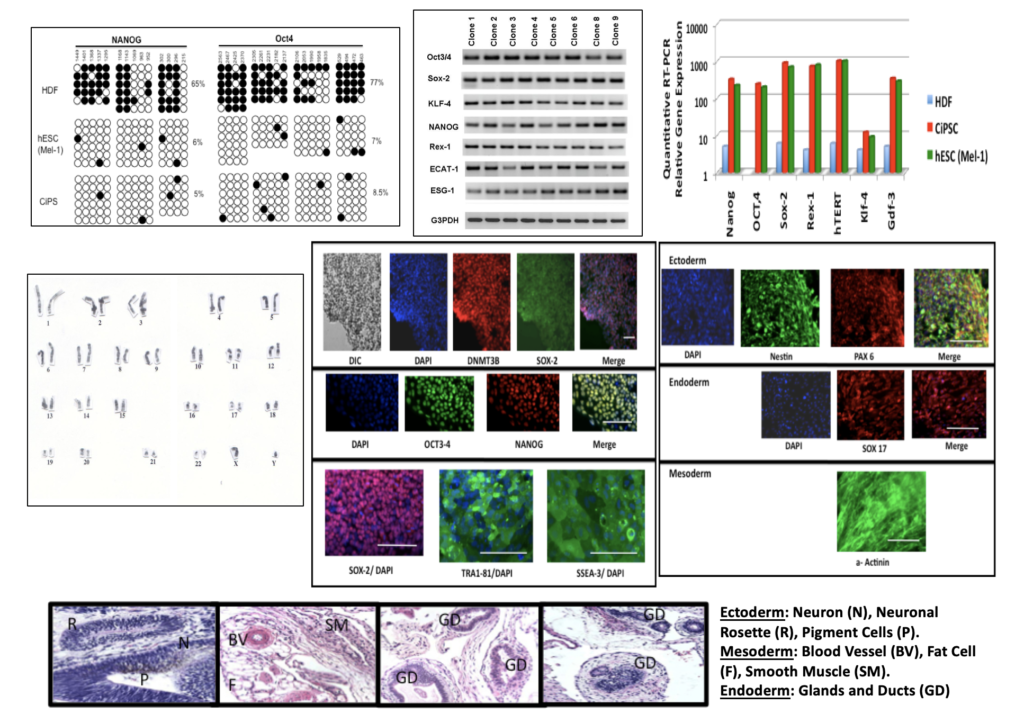
Validaton of CiPSC "Complete" and "Partial" Reprogramming Drugs in-vitro & in-vivo (animal models of rejuvenation & biological age reversal).
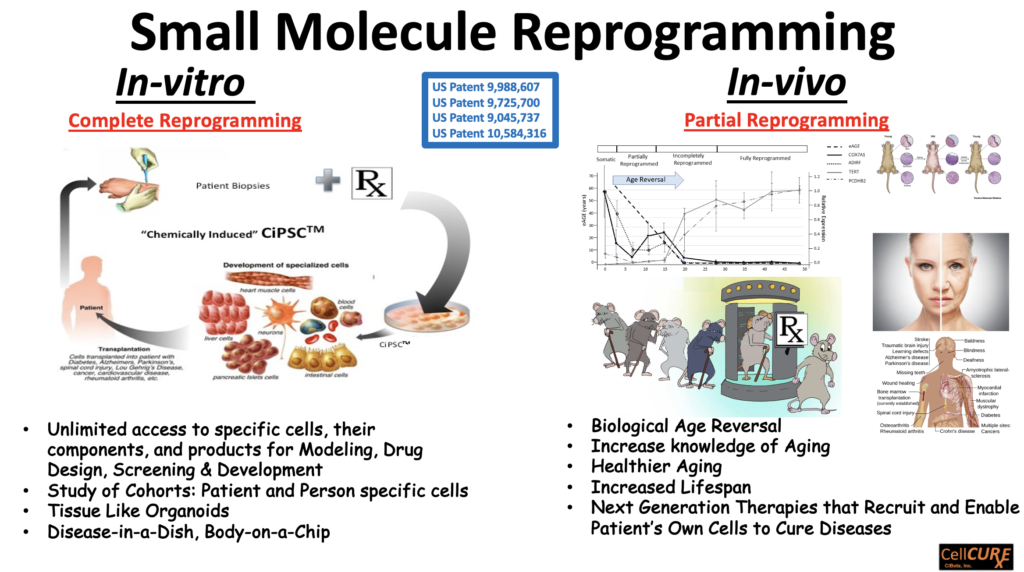
Use of small molecule drugs to induce and enhance partial reprogramming in-vivo has multiple advantages as a much safer alternative (clinically feasible prophylactic therapeutics) for aging: Cell dedifferentiation activity/ partial reprogramming level is readily fine-tuned by varying the concentrations of the drug(s). If necessary the application of lineage-alternating drugs could induce cell differentiation and inhibit undesired cell proliferation. Small molecule drugs are very feasible for non-immunogenic, cost-efficient, with minimal if any residual effects on the genome, and high feasibility of in-vivo application and clinical development. In addition to our therapeutic developments, we offer services of using aspects of this technology for small molecule “only”(no genetic factors) reprogramming and differentiation of human and animal somatic or stem cells. Patient specific tissue organoid cultures and cell lines are also “made to order” to build disease models for human disorders, drug toxicity testing, personalized medicine, and to develop next generation more efficacious & safer pharmaceuticals. For more information please visit our services page.
**CiPSC is a registered trademark of CiBots, Inc.
Further Readings:
2. Stem cell aging: mechanisms, regulators and therapeutic opportunities.
3. Extracellular matrix: A dynamic microenvironment for stem cell niche.
4. The role of microenvironment and immunity in drug response in leukemia.
5. The extracellular matrix niche microenvironment of neural and cancer stem cells in the brain.
6. Mesenchymal stem cells, aging and regenerative medicine.
7. Questionable Young Blood Transfusions Offered in U.S. as Anti-Aging Remedy.
8. Young blood antiaging trial raises questions.
9. Stem Cell Transplantation for Frailty.
10. Anti-Aging Strategies Based on Cellular Reprogramming.
11. 3D niche microarrays for systems-level analyses of cell fate.
12. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and Disease.
13. Dissecting the stem cell niche with organoid models: an engineering-based approach.

